Differences between CELF and Excel sheet specifications¶
This page describes the main differences in specifications for features and functions that exist in both CELF sheets and Excel sheets.
Attention
- The contents of this page do not cover all the specification differences between CELF and Excel.
- Depending on the version of Excel, the behavior may differ from the explanation on this page.
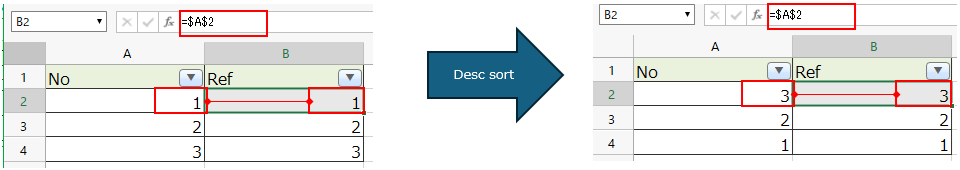
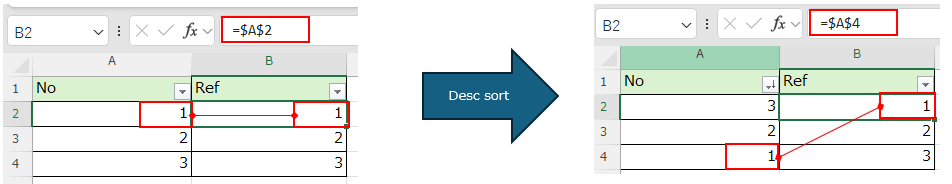
Absolute reference cells after sorting by filter button¶
Numeric (floating point) precision¶
The comparison result of the formula "=0.1+0.1+0.1=0.3" is "FALSE".
The comparison result of the formula "=0.1+0.1+0.1=0.3" is "TRUE".
Handling of "February 29" (leap year) in 1900¶
If the formula "=DATE(1900,3,0)" is entered to find the end of the month "February 1900" with the DATE function, "1900-02-28" will be displayed.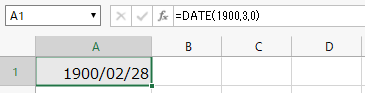
If the formula "=DATE(1900,3,0)" is entered to find the end of the month "February 1900" with the DATE function, "1900-02-29" will be displayed.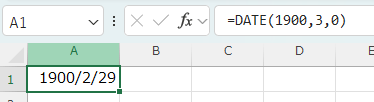
See also
See the Microsoft Troubleshooting on why Excel evaluates the year 1900 as a leap year.
Behavior of numbers with more than 16 significant digits¶
If "1234567890123456" is entered in the cell, "1234567890123456" will be displayed.Attention
However, the following functions round the value to 15 significant digits and then evaluate the value or show the result.
- ROUND
- ROUNDDOWN
- ROUNDUP
- MROUND
- FLOOR
- CEILING
- INT
If "1234567890123456" is entered in the cell, "1234567890123450" will be displayed.
Operation when comparing a "number" with a "numeric string" using the comparison operator¶
If you enter '=123="123"' in the cell, the formula evaluates to TRUE.
If you enter '=123="123"' in the cell, the formula evaluates to FALSE.
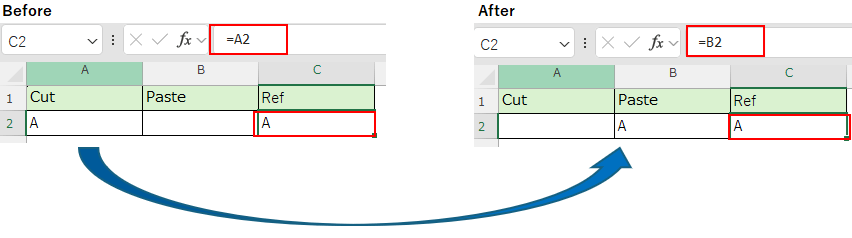
Automatic update of cells that reference Cut & Pasted cells¶
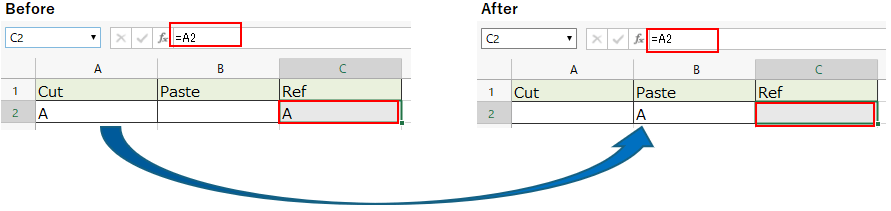
Tip
This behavior also applies to dragging and dropping cells.
Behavior when the cell value specified as the function argument is blank¶
Cells with blank value are handled as empty string (""), so they are evaluated as " =DAY("")" and the result is "#VALUE!".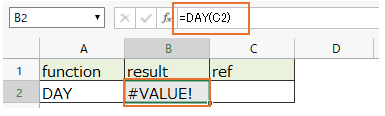
Cells with blank value are handled as "0", so they are evaluated as " =DAY(0)" and the result is "0".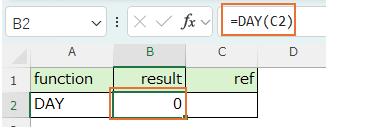
Attention
To get the same result as in Excel, make sure the cell value is not a blank or an empty string ("").
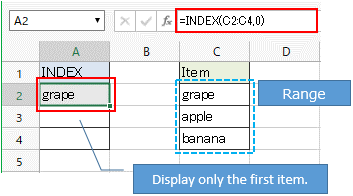
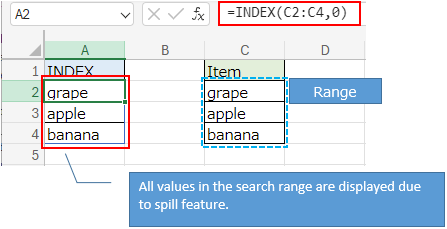
About spill and arrays¶
ex.) When "0" is specified for the 2nd argument (row number) of the INDEX function
AVERAGEA function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when there are cells with blank value¶
Cells with blank value are handled as "0", so they are evaluated as "(100 + 0 + 200) / 3" and the result is "100".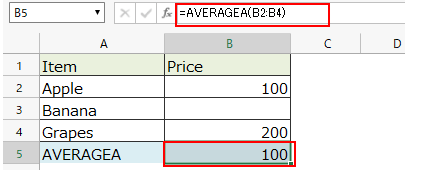
Cells with blank value are excluded, so they evaluate to "(100 + 200) / 2" and the result is "150".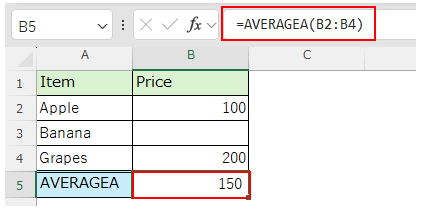
COUNTA function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when a formula exists in the specified range¶
If the result of the formula is an empty string, the result will be displayed without counting that cell.
Always count cells and display the result, regardless of whether result of the forumla is an empty string or not.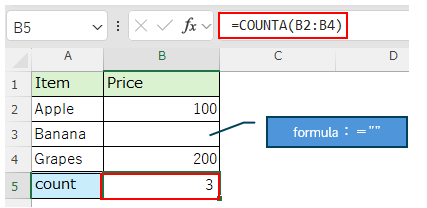
ISBLANK function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when the referenced cell is a formula¶
If the result of the formula is an empty string, the result is "true".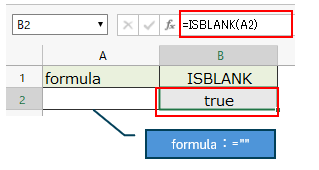
Regardless of whether the result of the formula is an empty string, the result will be "false".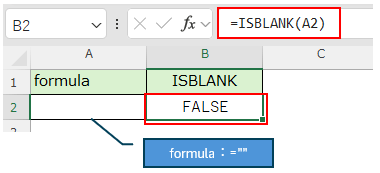
SUBTOTAL function behavior¶
Difference in behavior of aggregation method (1st argument)¶
If you specify the aggregation method "9" (SUM), the total will be calculated excluding hidden rows.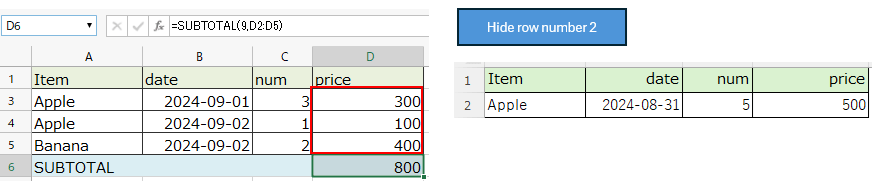
If you specify the aggregation method "9" (SUM), the total will include hidden rows.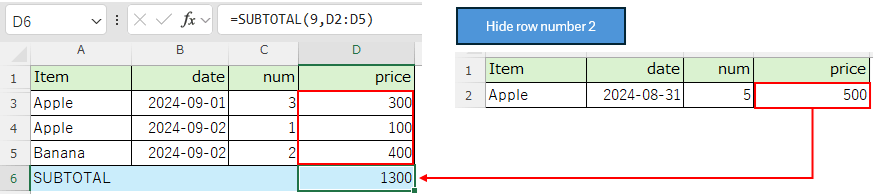
SUMIF function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when an empty cell( blank, or "") is specified for the search condition (2nd argument)¶
Matches cells in the range with empty value(blank or "") and the result is the sum of cells with empty values.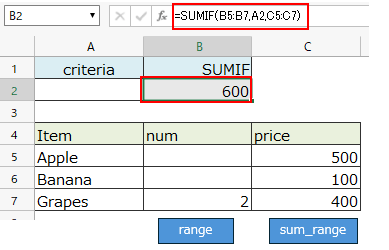
It will not match any cell with empty value in the range and the result will be "0".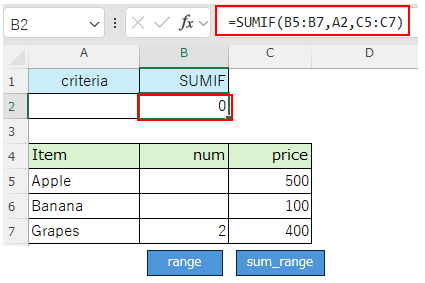
COUNTIF function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when an empty cell( blank, or "") is specified for the search condition (2nd argument)¶
Matches cells with empty value in the range and the result is the number of cells with empty value.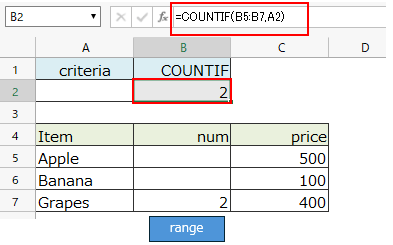
It will not match any cell with empty value in the range and the result will be "0".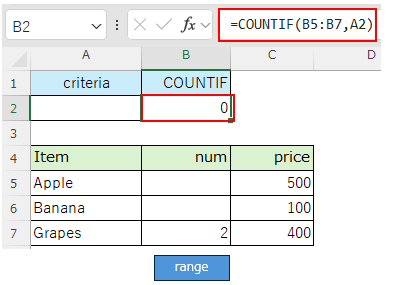
MROUND function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when "0" is specified for the multiplier (2nd argument)¶
The result of the formula "=MROUND(1,0)" is "#DIV/0!".
The result of the formula "=MROUND(1,0)" is "0".
CEILING function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when "0" is specified for the significance (2nd argument)¶
The result of the formula "=CEILING(1,0)" is "#DIV/0!".
The result of the formula "=CEILING(1,0)" is "0".
FLOOR function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when "0" is specified for the significance (2nd argument)¶
The result of the formula "=FLOOR(0,0)" is "#DIV/0!".
The result of the formula "=FLOOR(0,0)" is "0".
TRIM function behavior¶
Different whitespace characters to be deleted¶
The result is "ABC".
The result is "□ABC□".
Difference in behavior when there is a half-width space between characters¶
The result will be "ABC***DEF" (no change).
The result will be "ABC*DEF" (the consecutive spaces between the characters will be deleted to one).
VLOOKUP function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when "" or a cell with "empty value" is specified as the lookup value (1st argument)¶
If you specify a blank cell as the lookup value, it will match cells with empty value (blank or empty string "").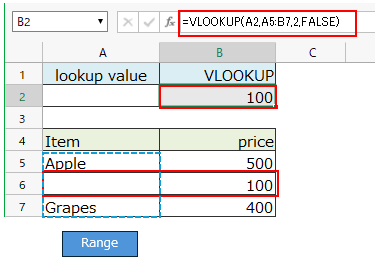
If you specify a cell with an empty value ("" or blank) as the lookup value, it will not match a cell with an empty value and the result will be "#N/A".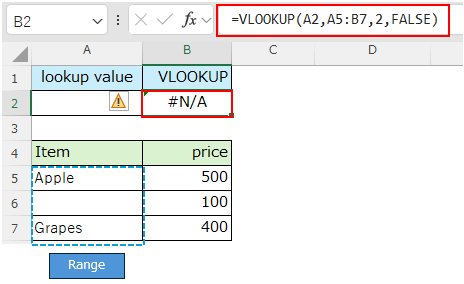
Differences in behavior when the values to be compared are "numbers" and "numeric strings"¶
If the lookup value is the string "2", it will match the cell with number 2 and the result will be "Apple".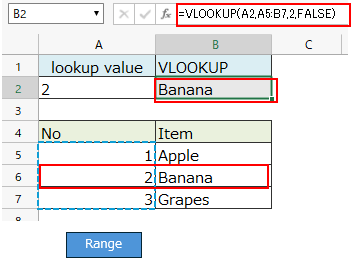
Tip
If the lookup value is the number 2, it will match not only the number 2 but also cells that contain the strings "2" and "002".
If the lookup value is the string "2", it will not match the number 2 in table array and the result will be "#N/A".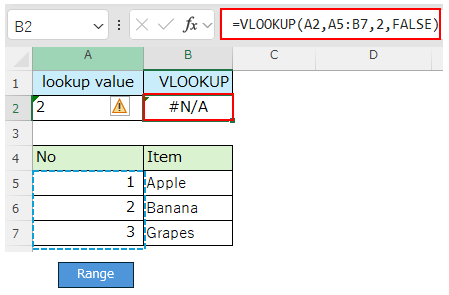
HLOOKUP function behavior¶
Difference in behavior when "" or a cell with "empty value" is specified as the lookup value (1st argument)¶
If you specify a blank cell as the lookup value, it will match cells with empty value (blank or empty string "").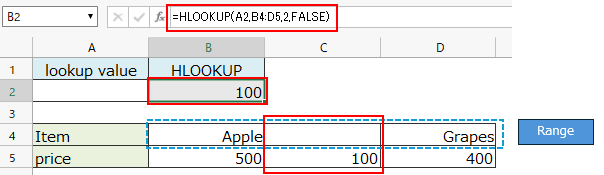
If you specify a cell with an empty value ("" or blank) as the lookup value, it will not match a cell with an empty value and the result will be "#N/A".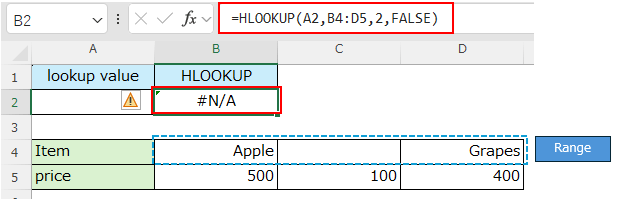
Differences in behavior when the values to be compared are "numbers" and "numeric strings"¶
If the lookup value is the string "2", it will match the cell with number 2 and the result will be "Apple".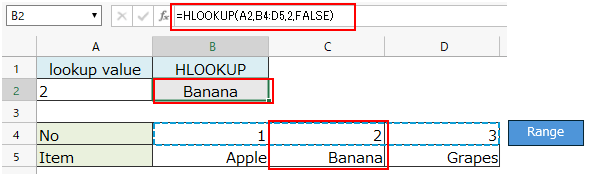
If the lookup value is the string "2", it will not match the number 2 in table array and the result will be "#N/A".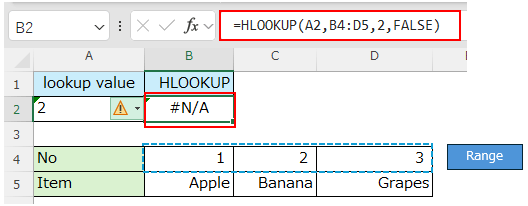
XLOOKUP function behavior¶
Differences in behavior when the values to be compared are "numbers" and "numeric strings"¶
If the lookup value is the string "2", it will match the cell with number 2 and the result will be "Apple".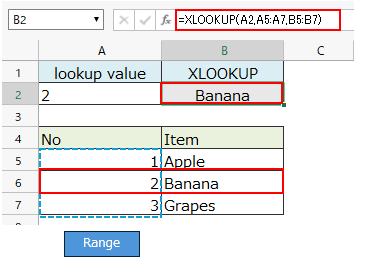
If the lookup value is the string "2", it will not match the number 2 in table array and the result will be "#N/A".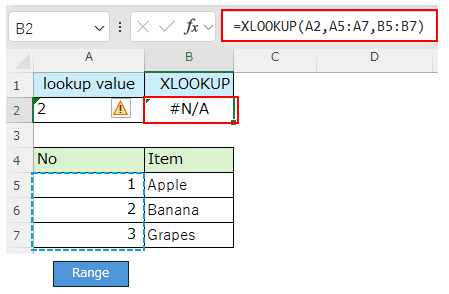
Difference in the value returned by the return array (3rd argument)¶
If an XLOOKUP function is specified as the reference for the ROW function, the ROW function will not be evaluated even if there is a value matching the lookup value.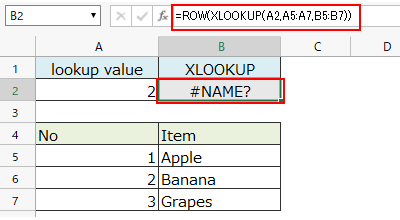
If an XLOOKUP function is specified as the reference for the ROW function, the ROW function will evaluate the matched value if it matches the lookup value.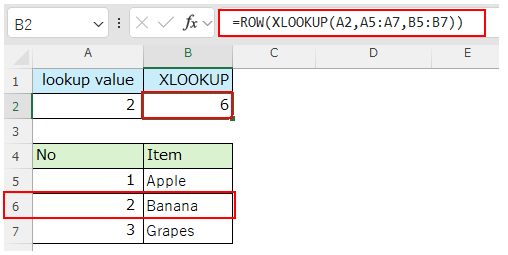
Difference in behavior when "2" is specified for the match mode (5th argument)¶
If "2" is specified for the match mode (5th argument), the result will be "#VALUE!".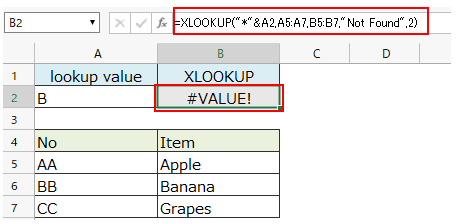
Tip
If you want to perform a fuzzy search such as a partial match, please consider methods like using the "Get one record from table" action to search.
If "2" is specified for the match mode (5th argument), fuzzy search will be performed.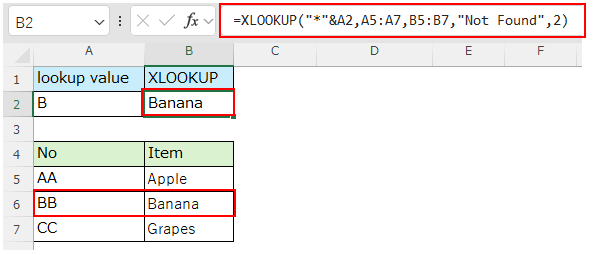
MATCH function behavior¶
Differences in behavior when specifying "0" for the match type (third argument)¶
In Excel, the MATCH function allows the use of wildcards for the lookup value when "0" is specified for the match type (third argument). However, the MATCH function in CELF does not support this.Therefore, even when using wildcards, the search is performed with the entered string as it is, resulting in "#N/A".
When a string that uses wildcards is specified as the lookup value, it searches for the exact input string, resulting in "#N/A".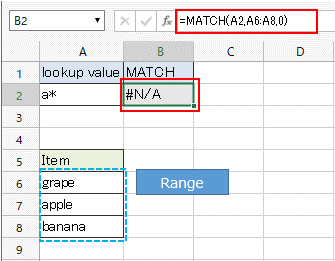
Tip
If you want to perform a fuzzy search such as a partial match, please consider methods like using the "Get one record from table" action to search.
When a string that uses wildcards is specified as the lookup value, a fuzzy search is performed.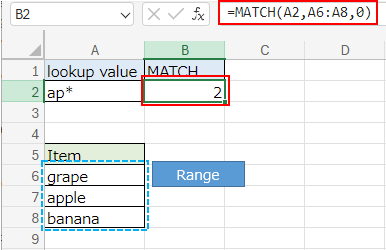
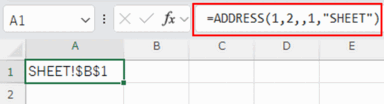
ADDRESS function behavior¶
Differences in behavior when the sheet name (fifth argument) is specified, but the reference type (third argument) or reference style (fourth argument) is omitted.¶
If the reference type (third argument) is omitted, the result will be "#VALUE!".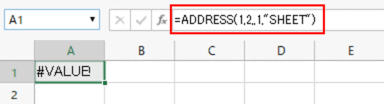
Tip
If the sheet name (fifth argument) is specified, providing both the reference type (third argument) andthe reference style (fourth argument) ensures that the result matches that of Excel.
When the reference type (third argument) is omitted, the result will be displayed as "SHEET!$B$1".