SQL Action (Extension option)¶
See also
Regarding registration of new extension option, refer to Register new extension option .
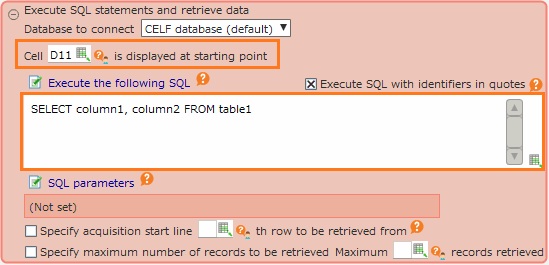
Retrieve data from a table using SQL¶
Write the SQL that is to be executed in the input field and save the action set. The acquired data is displayed at from the specified cell.
Attention
Set one SQL statement in one action.
- Please specify the column name that is to be acquired. The cells appear in the order in which you enter them.It is also possible to acquire all columns using "* (asterisk)", but the order of acquired columns is not guaranteed.
SQL other than SELECT statement can not be registered. Please use Actions related to data operation for registration, update, and deletion.
- When embedding values into SQL at runtime, such as using user input values as search criteria, be sure to use the parameters described below.When SQL statements are constructed using string concatenation, there is a risk of unintended data being accessed due to SQL injection.For information on SQL injection, please refer to the following.The OWASP® Foundation: https://owasp.org/www-community/attacks/SQL_Injection
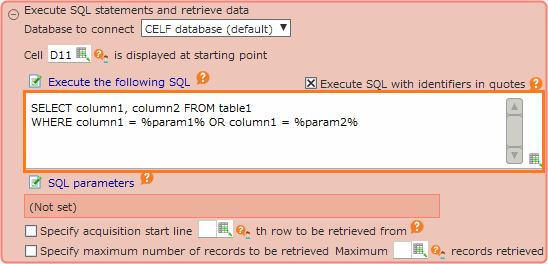
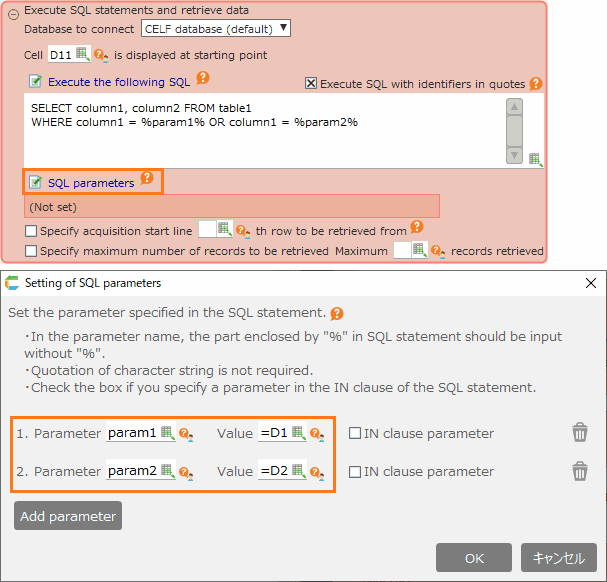
Specify search conditions with parameters¶
Within the SQL statement, you can set condition values by specifying parameters. Write the parameter name (any string) enclosed in "%" in the SQL statement.
Attention
SQL parameter names can only contain half-width alphanumeric characters
Set the value corresponding to the parameter name in the "Setting of SQL parameters" dialog.
Hint
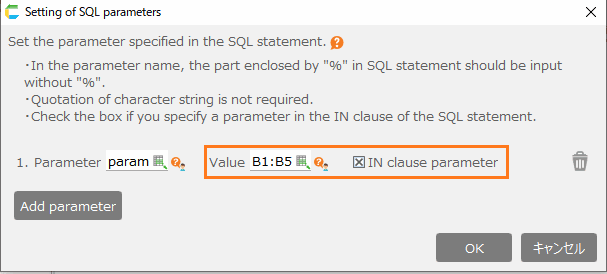
- If you want to set the parameter within the IN clause, check "IN clause parameter" and set the cell range to the value.
About the "Execute SQL with identifiers in quotes" option¶
Turn ON the "Execute SQL with identifiers in quotes" checkbox
For SQL actions, a "Execute SQL with identifiers in quotes" check was added in version 1.0.11.If this check is ON, only identifiers with the same name as the reserved words newly added in MySQL 8.0 will be executed with backquotes, thus avoiding errors.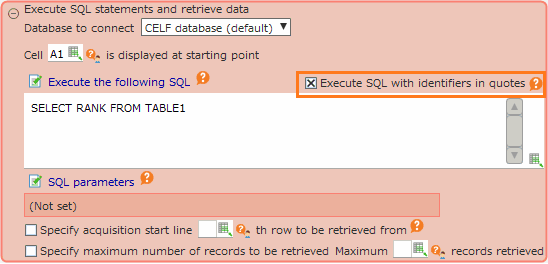
Tip
- The "Execute SQL with identifiers in quotes" is available only when "CELF database (default)" is selected in the destination database.
- For SQL actions created in versions prior to 1.0.10, the default value for "Execute SQL with identifier in quotes" is ON.
Enclose the identifier in backquotes as applicable
The error can be avoided by enclosing the appropriate identifier in backquotes as follows.e.g.)SELECT RANK FROM TABLE1 -> SELECT `RANK` FROM TABLE1SELECT COL1 AS RANK FROM TABLE1 -> SELECT COL1 AS `RANK` FROM TABLE1SELECT COL1 FROM RANK -> SELECT COL1 FROM `RANK`SELECT COL1 FROM TABLE1 RANK -> SELECT COL1 FROM TABLE1 `RANK`
Attention
If the version of the SQL action is 1.0.10 or lower, enclosing identifiers in backquotes will result in a syntax error.
See also
New reserved words added in MySQL 8.0 can be found at MySQL 8.0 New Keywords and Reserved Words.Words displayed on the linked page with "(R)" at the end are reserved words.
Notes regarding SQL actions¶
For SQL statements, it follows the SQL standard. Therefore, the following restrictions apply.
- Database-specific syntax may not be available.
- Some characters can not be used for column names and table names.
- If your SQL action version is less than 1.0.7, tables and columns whose names start with a number, dollar, or underscore are not available.
You can not use a function with the same name as a SQL reserved word. (Example: LEFT function, RIGHT function)
Specify an alias for columns retrieved in the SELECT clause if any of the following conditions apply.
- When column names in the SQL statement are duplicated due to table joins etc.e.g. SELECT t1.column1 AS t1_column1, t2.column1 AS t2_column1 FROM table1 t1, tabel2 t2
- When retrieving items other than table columns (as in the cases below)
- When retrieving fixed values such as numbers, strings, empty strings, etc.e.g. SELECT 123 AS int_val, 'abc' AS str_val, '' AS empty_val FROM table1
- When retrieving the results of functions or operationse.g. SELECT CONCAT(column1, 'abc') AS concat_val, column1 + 123 AS sum_val FROM table1
- When retrieving values using a CASE statemente.g. SELECT CASE WHEN column1 = 'a' THEN 1 ELSE 2 END AS case_val FROM table1
- In addition to CELF databases, you can also use external database tables with ODBC and JDBC connections.However, when merging tables, you are restricted to tables in the same destination database. (You can not link to other systems or other connection databases.)
- If you specify SQL as an expression or cell reference, you can not set up table switching at the time of publication beforehand.(If you enter SQL directly, table switching can be set.)However, if there are data manipulation-related actions for the same table in the same application, when table switching for that table is set,even if specified in a formula or cell reference, the SQL action will also work according to the set switching information.
The size limit for SQL statements is approximately 60,000 bytes. However, if there is a limit on the size of the connected database, that will be the upper limit.
- If the same table used in other actions is to be used in SQL, the table name must be the same case as the table name in the other action.If the case is different, the table switching tab of the "App Publication Settings" dialog will show the different case tables,and the same table cannot be specified as the switching destination.For more information on table switching, see Switch Unpublished or Published Table to be used by application
Permission check for SQL actions¶
The tables from which data can be retrieved using the SELECT statement executed in the SQL action are limited to those tables for which the updater of the sheet where the action set containing that SQL action is configured has reference permissions.
- The reference permission check is performed when the SQL action is executed. Please note that this timing differs from standard table reference action when checked at the time of creating an action set (during app creation).
- The following error occurs when attempting to retrieve data using a SELECT statement in an SQL action for a table that the sheet updater does not have referrence (read access) permissions for."SQLActionError: the SQL you executed contains a table for which you do not have access privileges."This error can be resolved in the following ways.
- Grant reference (read access) permission to the sheet updater for the table.Refer Set Permission for table Setting for information on setting table permissions.
- Overwrite and save the sheet with a user who has table reference permission.
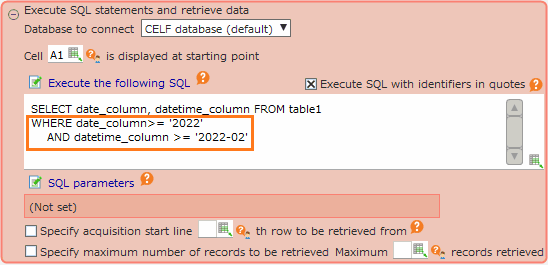
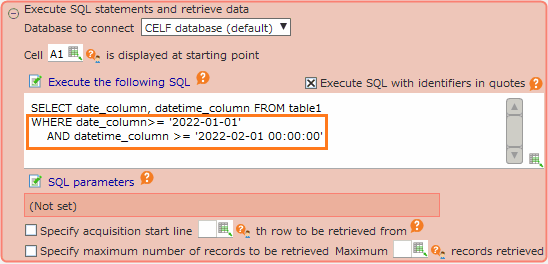
Notes on comparing date and date/time type columns and strings in MySQL¶
- When comparing to a string that cannot be interpreted as a date or datetime, such as '2022', '2022-02','' (blank), or''(space).
e.g.)
(DATE type column) >= '2022'(DATE type column) <= '2022-02'(DATETIME type column) <> ''(DATETIME type column) IN (' ')
See also
The standard CELF action auto-replaces strings when comparing strings that MySQL cannot interpret as dates or date/time.
Notes on writing SQL when using PostgreSQL¶
e.g.)
SELECT "column1" FROM "table1" -> SELECT column1 FROM table1
Small tricks / reverse-lookup on SQL action¶
- Retrieve data similar to SQL’s LEFT and RIGHT functions.
It is possible by expanding data into cells once and using CELF’s LEFT and RIGHT functions.Here’s how to set the CELF function as a string in SQL.
- Specify the following SQL in SQL action.
e.g.)SELECTcode As code ,"=LEFT(INDIRECT(ADDRESS(ROW(), COLUMN()-1)), 1)" AS initialFROM table1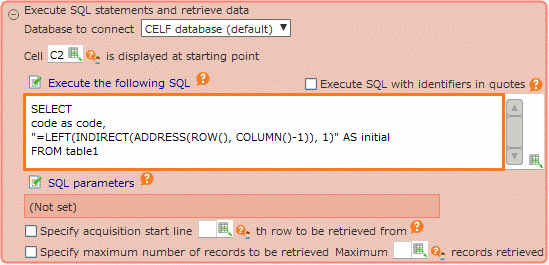
See also
For the INDIRECT function and ADDRESS function used here, please refer to Run Action Set when Cell Value Changed (Applied)
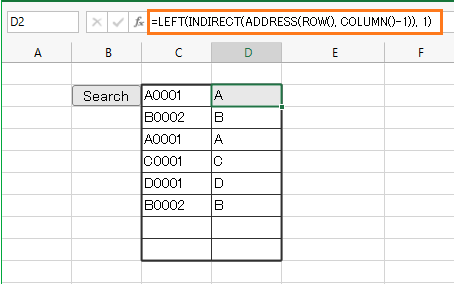
- Perform this action.
In column D, the function described in the SQL will be set directly in the cell, so the result of the functionexecution will be displayed.
Frequently Asked Questions about SQL Action¶
Here are some frequently asked questions about SQL actions.
[FAQ000142]When saving an action set using an action, the message "SQL is incorrect" is displayed
[FAQ000175]How do I confirm the SQL statement when executing an action?
[FAQ000141]How do I search for data that does not match when comparing two tables?